Introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving digital battlefield, staying ahead of cyber threats has become a real challenge, with recent incidents showing us that attackers are getting smarter and faster. For the teams on the front lines in security operations centers, it's like trying to find a needle in a massive haystack of alert. They're overwhelmed by security alerts, and a huge chunk of them turn out to be false positives, leading to a ton of wasted time trying to figure out what's a real threat versus what's just noise. As we look to the future, it's clear that artificial intelligence will be the next big thing in cyber warfare, based on Crowdstrike 2025 Global Threat Report, attackers using AI to launch more sophisticated attacks. The answer isn't to just fight fire with fire, but to create a smart partnership between AI-driven defense systems and human experts. By combining the speed and data-processing power of AI with the creative problem-solving and intuition of security professionals,
This article explores how integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) with human expertise can enhance the detection and response to such threats, aiming to streamline cybersecurity operations and mitigate risks effectively.
Leveraging AI: The Model Context Protocol (MCP) Workflow
We conducted an experiment to employ the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to automate and enrich the analysis of network traffic data to analyze Redline Stealer malware.
This approach enables swift identification of malicious activities while allowing human analysts to focus on critical decision-making, especially with malware like Redline Stealer, adversaries, and massive data volumes, making manual incident response alone a losing game.
Below is our technical workflow and use case from PCAP to insights when we conduct this experiment:
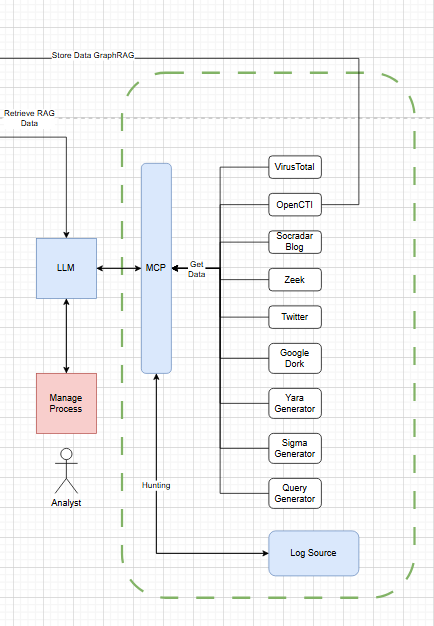
Technical Workflow Overview:
In this use case we have been experiment to implement the MCP to handling the cyber security cases.
- PCAP Handling and Analysis
- Utilize Zeek to parse network capture (PCAP) files, generating detailed logs for analysis.
- Log Processing and Data Enrichment
- Extract and validate records from Zeek logs to ensure data integrity.
- Threat Intelligence Correlation
- Use OpenCTI to correlate data with known malware, Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs), and Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs).
- VirusTotal Integration
- Enhance analysis accuracy by cross-referencing findings with VirusTotal's database.
- News and RAG Data
- Supplement findings with recent threat intelligence reports and public disclosures to provide context and better situational awareness of Redline Stealer’s latest campaigns, TTP evolutions, and industry impact.
- Human-in-the-Loop Decision Making
- Analysts validate AI-generated insights, assess relevance, and formulate response strategies, for example, Is this IoC linked to a known campaign, or is it a false positive?
- Response strategies (isolation, notification, escalation) are created by humans using the enriched dataset.
Sample Pcap get from this : https://www.malware-traffic-analysis.net/2024/10/23/index.html
Demonstration: MCP Workflow in Action
To illustrate the practical application of the MCP workflow, we've prepared a demonstration video showcasing the end-to-end process—from analyzing a PCAP file to deriving actionable insights.
MCP Workflow for Analyzing Cybersecurity Logs Demo
Using this workflow we are able to generate the following report:
Incident Analysis Report
Incident Summary:
The analysis of the provided pcap file revealed a potential malware infection related to the Redline Stealer. Two malicious IPs were identified: 188.190.10.10 (score: 9) and 172.67.75.172 (score: 1). The IP 188.190.10.10 is associated with the Redline Stealer malware.
IoCs:
- 188.190.10.10 (Malicious, score: 9)
- 172.67.75.172 (Malicious, score: 1)
Malware:
- win.redline_stealer
TTPs (win.redline_stealer):
- T1056.001 - Credential API Hooking
- T1555 - Credentials
- T1003 - Password Cracking
- T1041 - Exfiltration Over Web Service
- T1547.001 - Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder
- T1071.001 - Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols
Lucienne Query:
(index=network OR index=endpoint) AND (src_ip="188.190.10.10" OR dest_ip="188.190.10.10" OR src_ip="172.67.75.172" OR dest_ip="172.67.75.172")
Mitigation Plan:
1. Isolate the infected host (10.10.23.101) from the network to prevent further communication and potential data exfiltration.
2. Scan the host with an up-to-date antivirus solution to detect and remove the Redline Stealer malware.
3. Reset all user credentials that may have been compromised by the malware, including domain accounts, email accounts, and local machine accounts.
4. Monitor network traffic for any suspicious activity related to the identified IoCs.
5. Block the malicious IPs (188.190.10.10 and 172.67.75.172) at the firewall level
Recommendation:
1. Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all critical systems and accounts to prevent unauthorized access.
2. Educate users about phishing attacks and how to identify suspicious emails or websites.
3. Regularly update antivirus software and other security tools to protect against the latest threats.
4. Implement a strong password policy that requires users to create complex passwords and change them regularly.
5. Monitor network traffic for unusual patterns and potential data exfiltration attempts.
Findings: Enhancing Efficiency and Accuracy
The implementation of the AI-driven MCP workflow yielded significant improvements in threat detection and response times. By automating initial analysis phases, analysts could focus on critical evaluation and decision-making, effectively mitigating risks associated with AI inaccuracies or "hallucinations."
Key Outcomes:
- Improved Detection Speed: Automated processes expedited the identification of malicious activities.
- Enhanced Accuracy: Human oversight ensured the validity of AI-generated insights, reducing false positives.
- Resource Optimization: Streamlined workflows allowed for better allocation of human resources to complex tasks requiring expert judgment.
Conclusion: A Collaborative Path Forward
This research underscores the potential of combining AI capabilities with human expertise to fortify cybersecurity defenses. The MCP framework exemplifies how such collaboration can lead to more efficient and accurate threat detection and response mechanisms.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, embracing AI-human collaboration will be pivotal in maintaining robust security postures.


